The Evolution Of The Dark Web: From Anonymity To Criminal Activity
The Birth of the Dark Web: Anonymity and Privacy
The dark web was first created in the mid-1990s by the U.S. Navy to create a secure network for computers to exchange data with eachother, originally the dark web was a platform for intelligence and military personnel. The goal was to enable anonymous communication by using a set of various techniques implemented by the Tor network to protect sensitive data the government owns from interception. The foundational purpose of anonymity attracted early adopters of the dark web, who valued anonymity and privacy, including activists, journalists, and whistle-blowers operating in oppressive regimes. The technology behind the dark web, primarily the Tor network, allowed users to browser the internet and access hidden websites securely, fostering a sense of security and freedom.
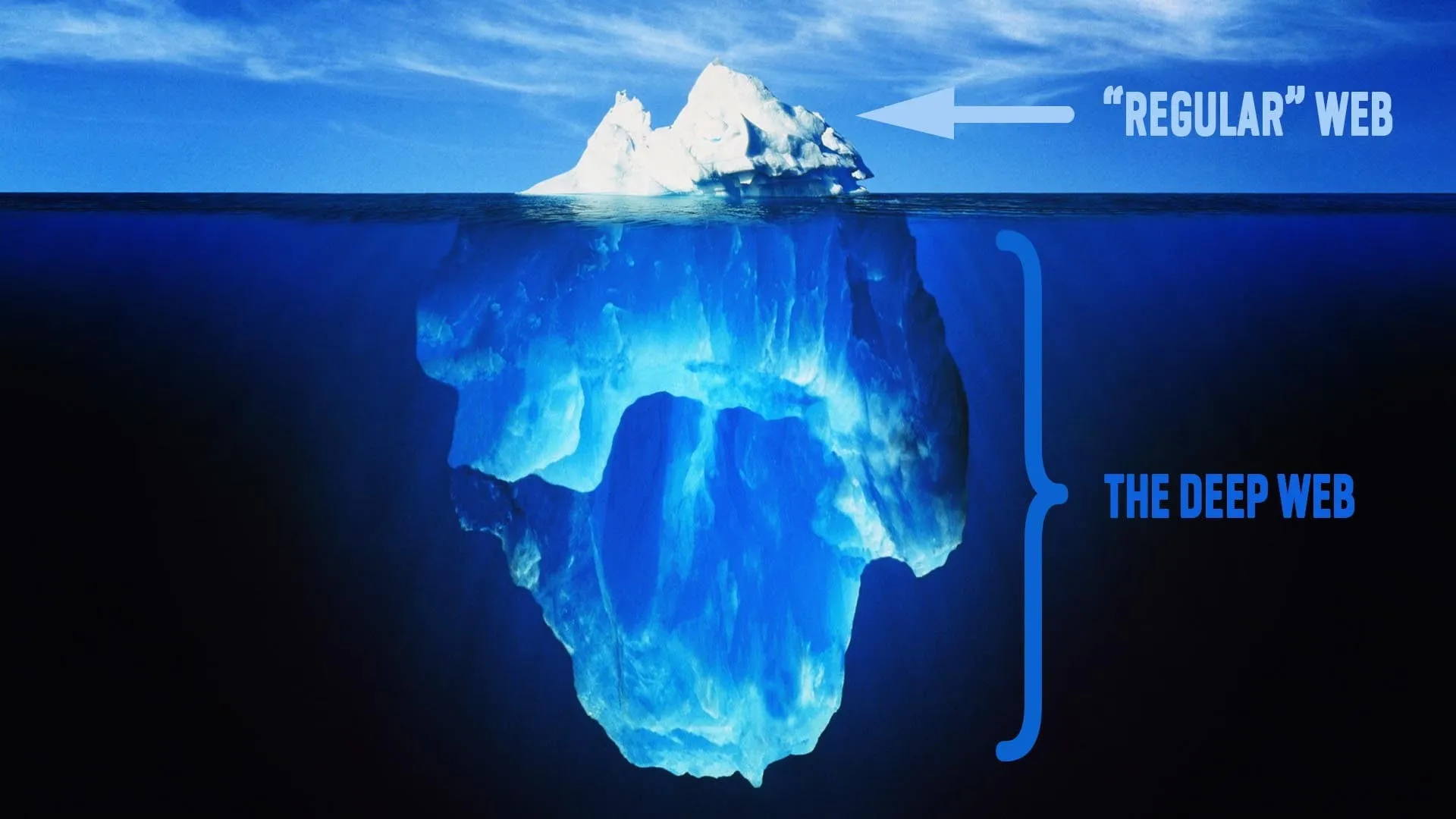
The Rise of Dark Web Marketplaces
As the dark web gained traction, it began to attract a different kind of user: those looking to engage in illicit activities. In 2011, a marketplace called Silk Road would rise, selling illegal goods including drugs, weapons and stolen data. The success of Silk Road demonstrated the potential for transactions to occur anonymously, leading to the emergence of many other marketplaces. The dark web's shift from being a space primarily focused on privacy to one rife with criminal activity highlighted the duality of the dark web, and why it is such a controversial point of discussion.
Law Enforcement and the Dark Web: A Game of Cat and Mouse
The rise of marketplaces on the dark web was not unnoticed by law enforcement agencies. As these platforms for exchanging illegal goods and services grew, authorities around the world began to develop strategies to combat the illegal activities taking place on the dark web. Over the course of the dark web's life, multiple high-profile operations - such as the take-down of Silk Road in 2013 - showcased the challenges law enforcement faced with navigating the complexities of the dark web. Despite the efforts made against these marketplaces, when one would fall a new one would simply fill the gap it left behind. The root of the issue law enforcement face is that these marketplaces only exist to serve a demand, and removing one will simply cause a new one to be created to fill the demand; this is a game of supply and demand. The ongoing battle between law enforcement agencies and the operators of illegal websites has created a cat-and-mouse dynamic, with each side adapting its tactics to combat the other.

The Dark Web as a Tool for Activism
While the dark web is often associated with crime and illicit material, it also serves as a necessary tool for activists and dissidents to securely communicate. Whistle-blowers who reside in oppressive regimes can use the dark web to securely communicate, share information and organize protests without fear of government surveillance. For example, during the Arab Spring, activists would use the technologies of the dark web to coordinate efforts and share information. This aspect of the dark web highlights the potential it has to be the platform of positive change and freedom, outlining the importance of anonymity in protecting human rights and freedom-of-expression.
The Future of the Dark Web: Balancing Privacy and Security
As the dark web continues to grow, the challenge remains to balance the risks of criminal activity with the need for privacy. With increasing scrutiny from law enforcement agencies, the future of the dark web may see a shift in its user base. While many argue for more regulations for the dark web, a concept that would be very difficult to implement, others advocate for the preservation of anonymity as a fundamental human right. The continued debate surrounding the dark web highlights broader societal issues in regards to security, privacy, human-rights and the role of technology in our lives. As we move forward, understanding the complexities of the dark web will be vital for navigating its implications for individuals and society as a whole.

17th September 2024